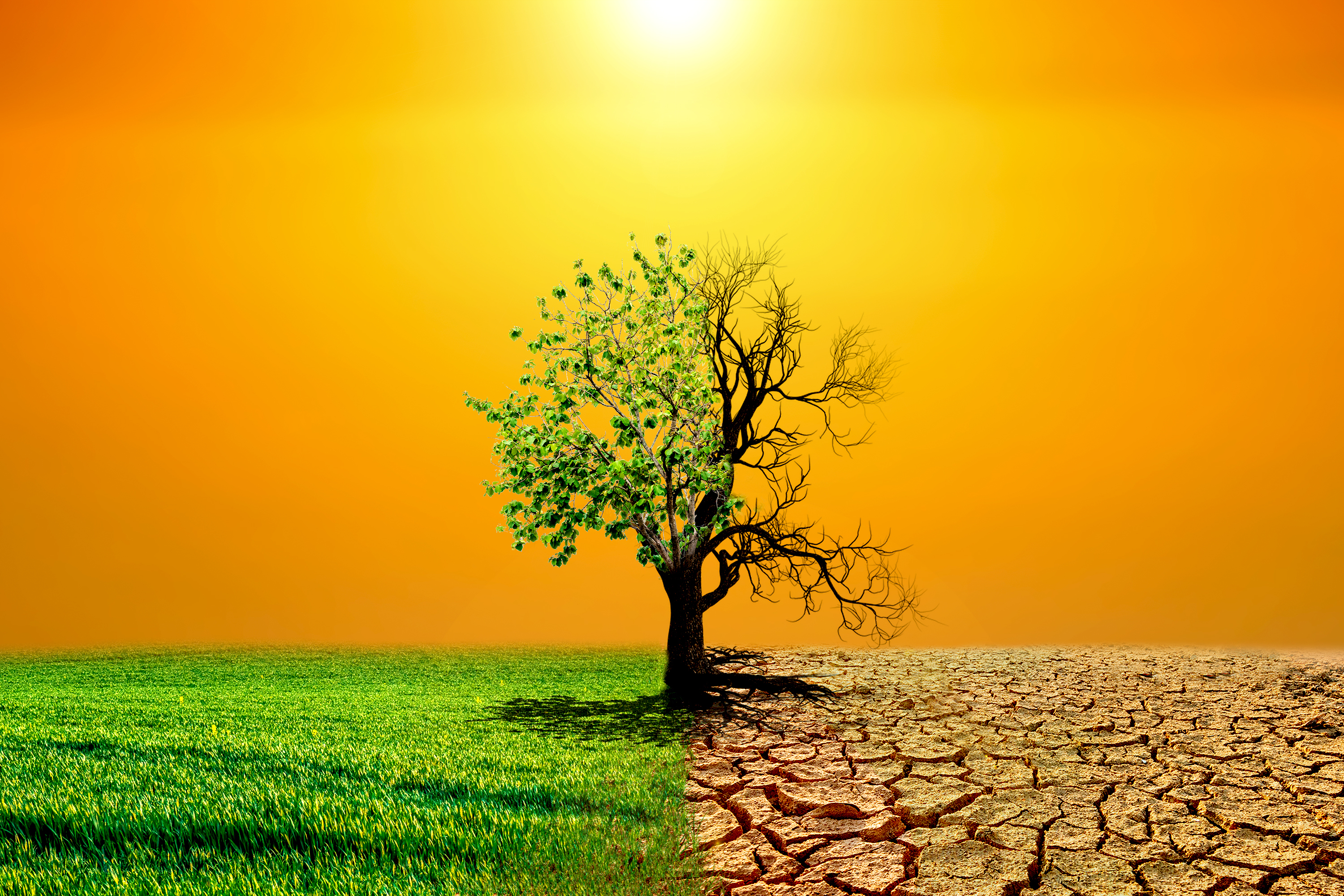
Global warming is an environmental phenomenon that has gained significant attention in recent decades. It refers to the long-term increase in the Earth's average surface temperature due to human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
To comprehend global warming, it is essential to grasp the concept of the greenhouse effect. The Earth's atmosphere contains naturally occurring gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O).
These gases act as a blanket, allowing sunlight to penetrate the atmosphere while trapping some of the heat radiating from the Earth's surface. This natural process is necessary for sustaining life on our planet, as it keeps the average temperature at a habitable level.
Impacts of Global Warming
a) Rising Temperatures: The most apparent consequence of global warming is the increase in average surface temperatures worldwide. This rise in temperature disrupts ecosystems, alters weather patterns, and impacts human health and agriculture.
b) Melting Glaciers and Rising Sea Levels: As temperatures increase, glaciers and ice caps melt, leading to rising sea levels. This phenomenon threatens coastal areas, increasing the risk of flooding, erosion, and salinization of freshwater sources.
c) Extreme Weather Events: Global warming intensifies the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, including hurricanes, heatwaves, droughts, and heavy rainfall. These events have devastating effects on human lives, infrastructure, agriculture, and ecosystems.
d) Biodiversity Loss: Changing climatic conditions force many species to migrate or adapt. However, the speed at which global warming is occurring makes it difficult for ecosystems and species to adjust, leading to biodiversity loss and potential ecosystem collapse.
e) Ocean Acidification: Increased CO2 absorption by the oceans causes acidification, threatening marine life, coral reefs, and shellfish populations. This impacts the entire marine food chain, affecting both ocean ecosystems and human communities that rely on them for sustenance and livelihood.
Global warming, an ongoing phenomenon, is primarily caused by human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. It has become one of the most pressing environmental concerns of our time, with significant implications for the planet and future generations.
This article aims to examine the various human activities contributing to global warming, their impacts, and the potential solutions available to mitigate this critical issue.
Fossil Fuel Consumption
The burning of fossil fuels for energy production, transportation, and industrial processes is the largest contributor to global warming. Carbon dioxide (CO2), a potent greenhouse gas, is released during the combustion of fossil fuels.
The accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere traps heat, leading to the greenhouse effect and subsequent global warming. Transitioning to cleaner and renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is crucial in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
Deforestation and Land Use Changes
Deforestation and land use changes have a significant impact on global warming. Trees act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and storing it in their biomass. However, when forests are cleared for agriculture, urbanization, or logging, the stored carbon is released into the atmosphere.
Additionally, the loss of trees reduces the planet's ability to absorb CO2, exacerbating the greenhouse effect. Implementing sustainable land management practices, reforestation efforts, and protecting natural habitats are essential in combating deforestation and preserving carbon sinks.
Agriculture and Livestock
Agriculture, particularly livestock production, contributes to global warming through multiple mechanisms. Livestock farming produces substantial amounts of methane (CH4), another potent greenhouse gas, primarily from enteric fermentation and manure management.
Additionally, the use of synthetic fertilizers in agriculture releases nitrous oxide (N2O), yet another potent greenhouse gas. Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices, reducing food waste, and promoting plant-based diets can help mitigate the emissions from the agricultural sector.
Industrial Processes and Waste Management
Industrial processes, including the production of cement, steel, and chemicals, contribute to global warming through the release of CO2 and other greenhouse gases.
Moreover, improper waste management, such as open burning and landfills, releases significant amounts of methane and CO2 into the atmosphere. Employing cleaner technologies, improving waste management practices, and promoting recycling and circular economy initiatives can substantially reduce emissions from industrial activities.
Impacts of Global Warming
Human activities that contribute to global warming have wide-ranging environmental, social, and economic impacts. Rising temperatures lead to the melting of polar ice caps, causing sea-level rise and increased coastal flooding.
Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, heatwaves, and droughts, are becoming more frequent and intense. Changes in precipitation patterns and disruptions to ecosystems further threaten biodiversity and food security.
Additionally, global warming poses risks to human health, including the spread of diseases and increased heat-related illnesses.
Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing global warming requires a multi-faceted approach involving governments, businesses, communities, and individuals. Here are some key solutions and mitigation strategies:
Transition to Renewable Energy: Increasing the share of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease CO2 emissions.
Energy Efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industrial processes can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable Land Use: Protecting forests, promoting reforestation, and implementing sustainable agriculture and land management practices can help sequester carbon and preserve natural carbon sinks.
Green Transportation: Encouraging the use of public transportation, electric vehicles, and active modes of transport like walking and cycling can reduce emissions from the transportation sector.
Circular Economy: Promoting recycling, reducing waste generation, and implementing sustainable waste management practices can help minimize greenhouse gas emissions from industrial and municipal waste.
Policy Interventions: Governments should enact and enforce policies that encourage emission reductions, support renewable energy deployment, and incentivize sustainable practices.
Climate Education and Awareness: Raising public awareness about global warming and its impacts is crucial for driving individual and collective action to combat the issue.
Human activities significantly contribute to global warming, causing severe environmental, social, and economic impacts. Understanding the role of fossil fuel consumption, deforestation, agriculture, industrial processes, and waste management is essential in addressing this critical issue.
By transitioning to renewable energy sources, adopting sustainable land use practices, improving industrial processes, and implementing policy interventions, we can mitigate global warming and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Taking collective action is imperative to safeguard the planet and ensure a habitable environment for future generations.